| Brodmann area 24 | |
|---|---|
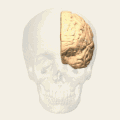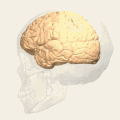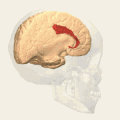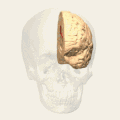
 Brodmann area 24 (shown in orange) | |
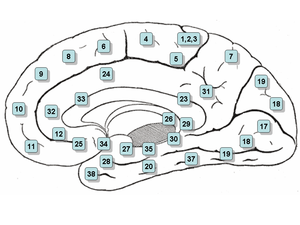 Brodmann areas - Medial surface. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Cingulate gyrus |
| Artery | Anterior cerebral |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | area cingularis anterior ventralis |
| NeuroNames | 2113, 1007 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1755 |
| FMA | 68621 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Brodmann area 24 is part of the anterior cingulate in the human brain.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:314 4952 644 20451 86714 784877
-
Cerebral cortex | Organ Systems | MCAT | Khan Academy
-
Meet Your Master: Getting to Know Your Brain - Crash Course Psychology #4
-
066 The Anatomy and Function of the Parietal Lobe
-
VÍDEO AULA NEUROANATOMIA CÓRTEX CEREBRAL PARTE 1
-
Neuroanatomia - Áreas Corticais
Transcription
Human
In the human this area is known as ventral anterior cingulate area 24, and it refers to a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined cingulate cortex region of cerebral cortex (area cingularis anterior ventralis). It occupies most of the anterior cingulate gyrus in an arc around the genu of the corpus callosum. Its outer border corresponds approximately to the cingulate sulcus. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded internally by the pregenual area 33, externally by the dorsal anterior cingulate area 32, and caudally by the ventral posterior cingulate area 23 and the dorsal posterior cingulate area 31.
Guenon
In the guenon this area is referred to as area 24 of Brodmann-1905. It includes portions of the cingulate gyrus and the frontal lobe. The cortex is thin; it lacks the internal granular layer (IV) so that the densely distributed, plump pyramidal cells of sublayer 3b of the external pyramidal layer (III) merge with similar cells of the internal pyramidal layer (V); the multiform layer (VI) is very thin (Brodmann-1905). Note that Brodmann later divided this area into two areas, area 24 of Brodmann-1909 and area 25 of Brodmann-1909 (Brodmann-1909).
Subdivisions
The area has been subdivided further, and Vogt et al.[1] distinguish three divisions of the area in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta):
- 24a: "adjacent to the callosal sulcus"
- 24b: "has more clearly defined layers II, III, and Va"
- 24c: "the lower bank of the anterior cingulate sulcus"
Image
-
Animation.
-
Medial view.
See also
Notes
- ^ Brent A. Vogt, Deepak N. Pandya, Douglas L. Rosene, "Cingulate cortex of the rhesus monkey: I. Cytoarchitecture and thalamic afferents," The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 262(2):256-270, 1987 doi:10.1002/cne.902620207.