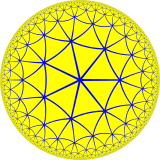
| Order-7 heptagrammic tiling | |
|---|---|
 Poincaré disk model of the hyperbolic plane | |
| Type | Hyperbolic regular tiling |
| Vertex configuration | (7/2)7 |
| Schläfli symbol | {7/2,7} |
| Wythoff symbol | 7 | 7/2 2 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [7,3], (*732) |
| Dual | Heptagrammic-order heptagonal tiling |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, face-transitive |
In geometry, the order-7 heptagrammic tiling is a tiling of the hyperbolic plane by overlapping heptagrams.
Description
This tiling is a regular star-tiling, and has Schläfli symbol of {7/2,7}. The heptagrams forming the tiling are of type {7/2}, ![]() . The overlapping heptagrams subdivide the hyperbolic plane into isosceles triangles, 14 of which form each heptagram.
. The overlapping heptagrams subdivide the hyperbolic plane into isosceles triangles, 14 of which form each heptagram.
Each point of the hyperbolic plane that does not lie on a heptagram edge belongs to the central heptagon of one heptagram, and is in one of the points of exactly one other heptagram. The winding number of each heptagram around its points is one, and the winding number around the central heptagon is two, so adding these two numbers together, each point of the plane is surrounded three times; that is, the density of the tiling is 3.
In the Euclidean plane, a heptagram of type {7/2} would have angles of 3π/7 at its vertices, but in the hyperbolic plane heptagrams can have the sharper vertex angle 2π/7 that is needed to make exactly seven other heptagrams meet up at the center of each heptagram of the tiling.
Related tilings
It has the same vertex arrangement as the regular order-7 triangular tiling, {3,7}. The full set of edges coincide with the edges of a heptakis heptagonal tiling. The valance 6 vertices in this tiling are false-vertices in the heptagrammic one caused by crossed edges.
It is related to a Kepler-Poinsot polyhedron, the small stellated dodecahedron, {5/2,5}, which is polyhedron and a density-3 regular star-tiling on the sphere:
References
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 19, The Hyperbolic Archimedean Tessellations)
- "Chapter 10: Regular honeycombs in hyperbolic space". The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays. Dover Publications. 1999. ISBN 0-486-40919-8. LCCN 99035678.
See also
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Hyperbolic tiling". MathWorld.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Poincaré hyperbolic disk". MathWorld.