| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
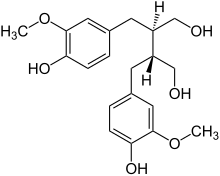
| IUPAC name
(8R,8′R)-3,3′-Dimethoxylignane-4,4′,9,9′-tetrol
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-2,3-Bis[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]butane-1,4-diol | |
| Other names
(−)-Secoisolariciresinol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.076 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H26O6 | |
| Molar mass | 362.422 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Secoisolariciresinol is an organic compound. It is classified as a lignan, i.e., a type of phenylpropanoid. It is present in some cereals, such as rye, and together with matairesinol has attracted much attention for its beneficial nutritional effects.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:1 406425 8503658 05480 621
-
❣ Top 9 Foods That Can Clean Your Arteries Naturally (& Prevent Heart Attack)
-
17 Health Benefits Of Cucumber
-
Farine minceur, oméga 3, Nopal, fibres, OPC et resvératrol : Fitolin
-
BATIDO VEGETAL SALUDABLE | Dr Nico Soto
-
Flaxseeds And Cancer Risk?
Transcription
Occurrence
The water extract of silver fir wood contains more than 5% of secoisolariciresinol.[2] It is also present in nettle brew.[3] Its content in flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) was found to be 0.3%,[4] which is the highest known content in food.
Biomedical aspects
In the intestine the gut microflora can form secoisolariciresinol from the secoisolariciresinol diglucoside and it can then be further transformed into the enterolignan enterodiol. Epidemiological studies showed associations between secoisolariciresinol intake and decreased risk of cardiovascular disease are promising, but they are yet not well established, perhaps due to low lignan intakes in habitual Western diets. At the higher doses used in intervention studies, associations were more evident.[5][6]
Glycosides
References
- ^ Seibel, Wilfried; Kim Chung, Okkyung; Weipert, Dorian; Park, Seok-Ho (2006). "Cereals". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_093.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Tavčar Benković, Eva; Žigon, Dušan; Mihailović, Vladimir; Petelinc, Tanja; Jamnik, Polona; Kreft, Samo (2017). "Identification, in vitro and in vivo Antioxidant Activity, and Gastrointestinal Stability of Lignans from Silver Fir (Abies alba) Wood Extract". Journal of Wood Chemistry and Technology. 37 (6): 467. doi:10.1080/02773813.2017.1340958. S2CID 90833072.
- ^ Francišković, Marina; Gonzalez-Pérez, Raquel; Orčić, Dejan; Sánchez de Medina, Fermín; Martínez-Augustin, Olga; Svirčev, Emilija; Simin, Nataša; Mimica-Dukić, Neda (August 2017). "Chemical Composition and Immuno-Modulatory Effects of Urtica dioica L. (Stinging Nettle) Extracts". Phytotherapy Research. 31 (8): 1183–1191. doi:10.1002/ptr.5836. ISSN 1099-1573. PMID 28544187. S2CID 33903986.
- ^ Milder, Ivon E. J.; Arts, Ilja C. W.; Putte, Betty van de; Venema, Dini P.; Hollman, Peter C. H. (2005). "Lignan contents of Dutch plant foods: a database including lariciresinol, pinoresinol, secoisolariciresinol and matairesinol". British Journal of Nutrition. 93 (3): 393–402. doi:10.1079/bjn20051371. ISSN 1475-2662. PMID 15877880.
- ^ Peterson, Julia; Dwyer, Johanna; Adlercreutz, Herman; Scalbert, Augustin; Jacques, Paul; McCullough, Marjorie L. (2010-10-01). "Dietary lignans: physiology and potential for cardiovascular disease risk reduction". Nutrition Reviews. 68 (10): 571–603. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00319.x. ISSN 0029-6643. PMC 2951311. PMID 20883417.
- ^ Pan, An; Yu, Danxia; Demark-Wahnefried, Wendy; Franco, Oscar H; Lin, Xu (2009-08-01). "Meta-analysis of the effects of flaxseed interventions on blood lipids". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 90 (2): 288–297. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.27469. ISSN 0002-9165. PMC 3361740. PMID 19515737.
