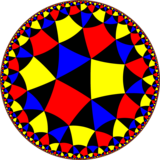
| Snub order-6 square tiling | |
|---|---|
 Poincaré disk model of the hyperbolic plane | |
| Type | Hyperbolic uniform tiling |
| Vertex configuration | 3.3.3.4.3.4 |
| Schläfli symbol | s(4,4,3) s{4,6} |
| Wythoff symbol | | 4 4 3 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [(4,4,3)]+, (443) [6,4+], (4*3) |
| Dual | Order-4-4-3 snub dual tiling |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
In geometry, the snub order-6 square tiling is a uniform tiling of the hyperbolic plane. It has Schläfli symbol of s{(4,4,3)} or s{4,6}.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/4Views:38397 5341 2671 033
-
Icosahedron
-
The Invisble Man by H.G. Wells (Full) with Subtitles + Text
-
Cambridge Talks IX: "Inscriptions of Power; Spaces, Institutions, and Crisis" Part 2
-
The Age of Innocence Audiobook by Edith Wharton | Audio book with subtitles
Transcription
Images
Symmetry
The symmetry is doubled as a snub order-6 square tiling, with only one color of square. It has Schläfli symbol of s{4,6}.
Related polyhedra and tiling
The vertex figure 3.3.3.4.3.4 does not uniquely generate a uniform hyperbolic tiling. Another with quadrilateral fundamental domain (3 2 2 2) and 2*32 symmetry is generated by ![]()
![]()
![]() :
:
| Uniform (4,4,3) tilings | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [(4,4,3)] (*443) | [(4,4,3)]+ (443) |
[(4,4,3+)] (3*22) |
[(4,1+,4,3)] (*3232) | |||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| h{6,4} t0(4,4,3) |
h2{6,4} t0,1(4,4,3) |
{4,6}1/2 t1(4,4,3) |
h2{6,4} t1,2(4,4,3) |
h{6,4} t2(4,4,3) |
r{6,4}1/2 t0,2(4,4,3) |
t{4,6}1/2 t0,1,2(4,4,3) |
s{4,6}1/2 s(4,4,3) |
hr{4,6}<sup>1</sup>/<sub>2</sub> hr(4,3,4) |
h{4,6}1/2 h(4,3,4) |
q{4,6} h1(4,3,4) |
| Uniform duals | ||||||||||

|

|

|

|
|||||||
| V(3.4)4 | V3.8.4.8 | V(4.4)3 | V3.8.4.8 | V(3.4)4 | V4.6.4.6 | V6.8.8 | V3.3.3.4.3.4 | V(4.4.3)2 | V66 | V4.3.4.6.6 |
| Uniform tetrahexagonal tilings | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [6,4], (*642) (with [6,6] (*662), [(4,3,3)] (*443) , [∞,3,∞] (*3222) index 2 subsymmetries) (And [(∞,3,∞,3)] (*3232) index 4 subsymmetry) | |||||||||||
= = = |
= |
= = = |
= |
= = = |
= |
||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||
| {6,4} | t{6,4} | r{6,4} | t{4,6} | {4,6} | rr{6,4} | tr{6,4} | |||||
| Uniform duals | |||||||||||
|
|

|

|

|

|

| |||||
| V64 | V4.12.12 | V(4.6)2 | V6.8.8 | V46 | V4.4.4.6 | V4.8.12 | |||||
| Alternations | |||||||||||
| [1+,6,4] (*443) |
[6+,4] (6*2) |
[6,1+,4] (*3222) |
[6,4+] (4*3) |
[6,4,1+] (*662) |
[(6,4,2+)] (2*32) |
[6,4]+ (642) | |||||
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||
| h{6,4} | s{6,4} | hr{6,4} | s{4,6} | h{4,6} | hrr{6,4} | sr{6,4} | |||||
See also
Footnotes
References
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 19, The Hyperbolic Archimedean Tessellations)
- "Chapter 10: Regular honeycombs in hyperbolic space". The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays. Dover Publications. 1999. ISBN 0-486-40919-8. LCCN 99035678.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Hyperbolic tiling". MathWorld.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Poincaré hyperbolic disk". MathWorld.
- Hyperbolic and Spherical Tiling Gallery
- KaleidoTile 3: Educational software to create spherical, planar and hyperbolic tilings
- Hyperbolic Planar Tessellations, Don Hatch