Schematic representation of difference in grain shape. Two parameters are shown: sphericity (vertical) and rounding (horizontal). Sphericity is a measure of how closely the shape of an object resembles that of a perfect sphere . For example, the sphericity of the balls inside a ball bearing determines the quality of the bearing, such as the load it can bear or the speed at which it can turn without failing. Sphericity is a specific example of a compactness measure of a shape . Defined by Wadell in 1935,[1]
Ψ
{\displaystyle \Psi }
surface area of a sphere with the same volume to the object's surface area:
Ψ
=
π
1
3
(
6
V
p
)
2
3
A
p
{\displaystyle \Psi ={\frac {\pi ^{\frac {1}{3}}(6V_{p})^{\frac {2}{3}}}{A_{p}}}}
where
V
p
{\displaystyle V_{p}}
A
p
{\displaystyle A_{p}}
unity by definition and, by the isoperimetric inequality , any shape which is not a sphere will have sphericity less than 1.
Sphericity applies in three dimensions ; its analogue in two dimensions , such as the cross sectional circles along a cylindrical object such as a shaft , is called roundness .
YouTube Encyclopedic
1 / 5
Views: 6 686
44 405
64 641
2 303
10 471
What is sphericity? Explained Simply
Mauchly's Test of Sphericity with Repeated Measures ANOVA in SPSS
SPHERICITY OF SOLID PARTICLES - UNIT OPERATIONS IN CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
Sphericity Explained Again With a Better Example
Ellipsoidal objects The sphericity,
Ψ
{\displaystyle \Psi }
oblate spheroid (similar to the shape of the planet Earth ) is:
Ψ
=
π
1
3
(
6
V
p
)
2
3
A
p
=
2
a
b
2
3
a
+
b
2
a
2
−
b
2
ln
(
a
+
a
2
−
b
2
b
)
,
{\displaystyle \Psi ={\frac {\pi ^{\frac {1}{3}}(6V_{p})^{\frac {2}{3}}}{A_{p}}}={\frac {2{\sqrt[{3}]{ab^{2}}}}{a+{\frac {b^{2}}{\sqrt {a^{2}-b^{2}}}}\ln {\left({\frac {a+{\sqrt {a^{2}-b^{2}}}}{b}}\right)}}},}
where a and b are the semi-major and semi-minor axes respectively.
Derivation Hakon Wadell defined sphericity as the surface area of a sphere of the same volume as the particle divided by the actual surface area of the particle.
First we need to write surface area of the sphere,
A
s
{\displaystyle A_{s}}
V
p
{\displaystyle V_{p}}
A
s
3
=
(
4
π
r
2
)
3
=
4
3
π
3
r
6
=
4
π
(
4
2
π
2
r
6
)
=
4
π
⋅
3
2
(
4
2
π
2
3
2
r
6
)
=
36
π
(
4
π
3
r
3
)
2
=
36
π
V
p
2
{\displaystyle A_{s}^{3}=\left(4\pi r^{2}\right)^{3}=4^{3}\pi ^{3}r^{6}=4\pi \left(4^{2}\pi ^{2}r^{6}\right)=4\pi \cdot 3^{2}\left({\frac {4^{2}\pi ^{2}}{3^{2}}}r^{6}\right)=36\pi \left({\frac {4\pi }{3}}r^{3}\right)^{2}=36\,\pi V_{p}^{2}}
therefore
A
s
=
(
36
π
V
p
2
)
1
3
=
36
1
3
π
1
3
V
p
2
3
=
6
2
3
π
1
3
V
p
2
3
=
π
1
3
(
6
V
p
)
2
3
{\displaystyle A_{s}=\left(36\,\pi V_{p}^{2}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}=36^{\frac {1}{3}}\pi ^{\frac {1}{3}}V_{p}^{\frac {2}{3}}=6^{\frac {2}{3}}\pi ^{\frac {1}{3}}V_{p}^{\frac {2}{3}}=\pi ^{\frac {1}{3}}\left(6V_{p}\right)^{\frac {2}{3}}}
hence we define
Ψ
{\displaystyle \Psi }
Ψ
=
A
s
A
p
=
π
1
3
(
6
V
p
)
2
3
A
p
{\displaystyle \Psi ={\frac {A_{s}}{A_{p}}}={\frac {\pi ^{\frac {1}{3}}\left(6V_{p}\right)^{\frac {2}{3}}}{A_{p}}}}
Sphericity of common objects
Name
Picture
Volume
Surface area
Sphericity
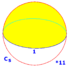
Sphere
4
3
π
r
3
{\displaystyle {\frac {4}{3}}\pi r^{3}}
4
π
r
2
{\displaystyle 4\pi \,r^{2}}
1
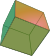
Disdyakis triacontahedron
180
11
(
5
+
4
5
)
s
3
{\displaystyle {\frac {180}{11}}\left(5+4{\sqrt {5}}\right)\,s^{3}}
180
11
179
−
24
5
s
2
{\displaystyle {\frac {180}{11}}{\sqrt {179-24{\sqrt {5}}}}\,s^{2}}
(
(
5
+
4
5
)
2
11
π
5
)
1
3
179
−
24
5
≈
0.9857
{\displaystyle {\frac {\left(\left(5+4{\sqrt {5}}\right)^{2}{\frac {11\pi }{5}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}}{\sqrt {179-24{\sqrt {5}}}}}\approx 0.9857}
Rhombic triacontahedron
4
5
+
2
5
s
3
{\displaystyle 4{\sqrt {5+2{\sqrt {5}}}}\,s^{3}}
12
5
s
2
{\displaystyle 12{\sqrt {5}}\,s^{2}}
π
1
3
(
24
5
+
2
5
)
2
3
12
5
≈
0.9609
{\displaystyle {\frac {\pi ^{\frac {1}{3}}\left(24{\sqrt {5+2{\sqrt {5}}}}\right)^{\frac {2}{3}}}{12{\sqrt {5}}}}\approx 0.9609}
Icosahedron
5
12
(
3
+
5
)
s
3
{\displaystyle {\frac {5}{12}}\left(3+{\sqrt {5}}\right)\,s^{3}}
5
3
s
2
{\displaystyle 5{\sqrt {3}}\,s^{2}}
(
(
3
+
5
)
2
π
60
3
)
1
3
≈
0.939
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {\left(3+{\sqrt {5}}\right)^{2}\pi }{60{\sqrt {3}}}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.939}
Dodecahedron
1
4
(
15
+
7
5
)
s
3
{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{4}}\left(15+7{\sqrt {5}}\right)\,s^{3}}
3
25
+
10
5
s
2
{\displaystyle 3{\sqrt {25+10{\sqrt {5}}}}\,s^{2}}
(
(
15
+
7
5
)
2
π
12
(
25
+
10
5
)
3
2
)
1
3
≈
0.910
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {\left(15+7{\sqrt {5}}\right)^{2}\pi }{12\left(25+10{\sqrt {5}}\right)^{\frac {3}{2}}}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.910}
Ideal torus
(
R
=
r
)
{\displaystyle (R=r)}
2
π
2
R
r
2
=
2
π
2
r
3
{\displaystyle 2\pi ^{2}Rr^{2}=2\pi ^{2}\,r^{3}}
4
π
2
R
r
=
4
π
2
r
2
{\displaystyle 4\pi ^{2}Rr=4\pi ^{2}\,r^{2}}
(
9
4
π
)
1
3
≈
0.894
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {9}{4\pi }}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.894}
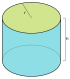
Ideal cylinder
(
h
=
2
r
)
{\displaystyle (h=2\,r)}
π
r
2
h
=
2
π
r
3
{\displaystyle \pi \,r^{2}h=2\pi \,r^{3}}
2
π
r
(
r
+
h
)
=
6
π
r
2
{\displaystyle 2\pi \,r(r+h)=6\pi \,r^{2}}
(
2
3
)
1
3
≈
0.874
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {2}{3}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.874}
Octahedron
1
3
2
s
3
{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{3}}{\sqrt {2}}\,s^{3}}
2
3
s
2
{\displaystyle 2{\sqrt {3}}\,s^{2}}
(
π
3
3
)
1
3
≈
0.846
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {\pi }{3{\sqrt {3}}}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.846}
Hemisphere
2
3
π
r
3
{\displaystyle {\frac {2}{3}}\pi \,r^{3}}
3
π
r
2
{\displaystyle 3\pi \,r^{2}}
(
16
27
)
1
3
≈
0.840
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {16}{27}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.840}
Cube (hexahedron)
s
3
{\displaystyle \,s^{3}}
6
s
2
{\displaystyle 6\,s^{2}}
(
π
6
)
1
3
≈
0.806
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {\pi }{6}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.806}
Ideal cone
(
h
=
2
2
r
)
{\displaystyle (h=2{\sqrt {2}}r)}
1
3
π
r
2
h
=
2
2
3
π
r
3
{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{3}}\pi \,r^{2}h={\frac {2{\sqrt {2}}}{3}}\pi \,r^{3}}
π
r
(
r
+
r
2
+
h
2
)
=
4
π
r
2
{\displaystyle \pi \,r(r+{\sqrt {r^{2}+h^{2}}})=4\pi \,r^{2}}
(
1
2
)
1
3
≈
0.794
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {1}{2}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.794}
Tetrahedron
2
12
s
3
{\displaystyle {\frac {\sqrt {2}}{12}}\,s^{3}}
3
s
2
{\displaystyle {\sqrt {3}}\,s^{2}}
(
π
6
3
)
1
3
≈
0.671
{\displaystyle \left({\frac {\pi }{6{\sqrt {3}}}}\right)^{\frac {1}{3}}\approx 0.671}
See also References External links
Look up
sphericity in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
This page was last edited on 8 December 2023, at 10:19












![{\displaystyle \Psi ={\frac {\pi ^{\frac {1}{3}}(6V_{p})^{\frac {2}{3}}}{A_{p}}}={\frac {2{\sqrt[{3}]{ab^{2}}}}{a+{\frac {b^{2}}{\sqrt {a^{2}-b^{2}}}}\ln {\left({\frac {a+{\sqrt {a^{2}-b^{2}}}}{b}}\right)}}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2fb6813ea9191eb0b12f73a7297468b55ff1351b)









































